Daily habits can be powerful. Routine anchors us and builds resilience and health. Adding a routine or mini-structure to your day so that fewer decisions need to be made is one way to succeed. When it comes to your health, preventing injuries in any activity you enjoy is crucial. Here are five injury-preventing exercises to put on your habit list that don’t take up too much time. Whether you are a seasoned athlete, or simply just enjoy being active but don’t want to get hurt, incorporate these moves into your day.
Activate the core: Heel on toe crunch
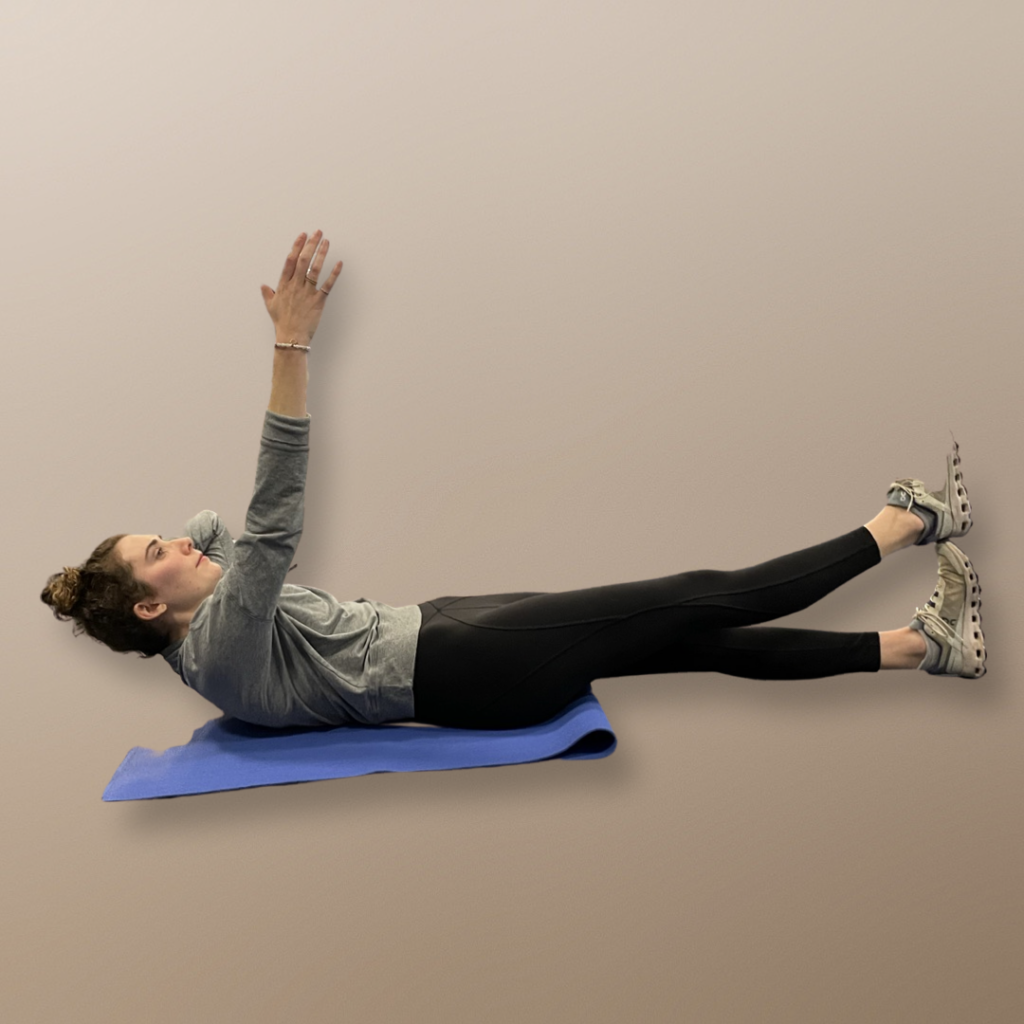

A demonstration of the heel-on-toe crunch. Photo courtesy of Connie Aronson
The core muscles help stabilize the spine and support movement. The following two core exercises have minimal movement, and are far more effective than a standard sit-up. The heel-on-toe crunch spares the back, while building muscular fitness. You begin the crunch by stiffening the abdominal muscles and slightly raising the head and shoulders off the ground. Count to 10, then lower back down to the starting position. To a viewer it might not look like you’re doing much of anything, says Stuart McGill, but with proper technique, you should feel like you’re working.
- Begin with your legs straight, left heel on top of right foot.
- Bring your left hand behind your head for support, and lift your right arm straight up from your shoulder.
- Curl up, raising your head, neck and shoulder blades off mat, tightening your abdominals.
- Slowly return to the start position. 10 reps. Switch sides.
Side lying hip lift
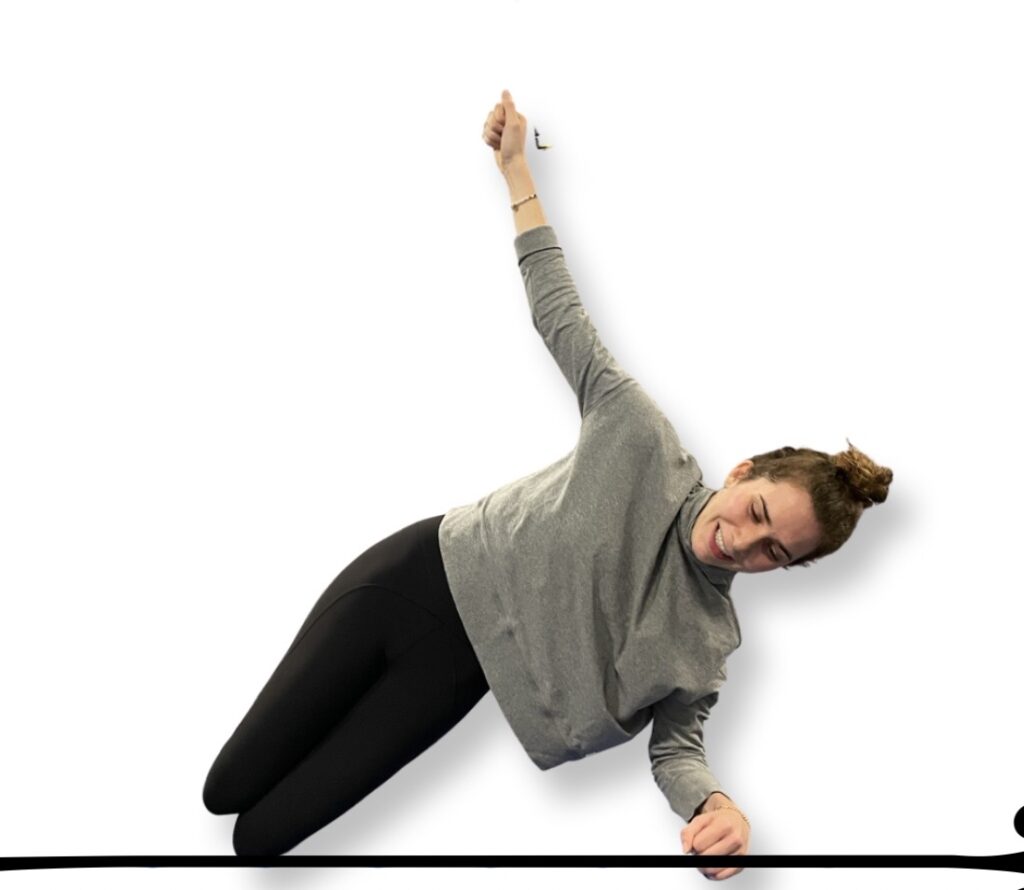

A demonstration of the side-lying hip lift. Photo courtesy of Connie Aronson
- Lying on your right side with your knees bent (or straight for advanced variation), place your right elbow under your right shoulder. Push your shoulder away from your ear to engage the shoulder girdle.
- Avoid letting your rib cage slump toward floor; maintain natural curve of spine.
- Exhale and lift your right hip off floor. Hold for 10 counts.
- Slowly lower to start. 6-8 reps. Switch sides.
Stretch tight hamstrings
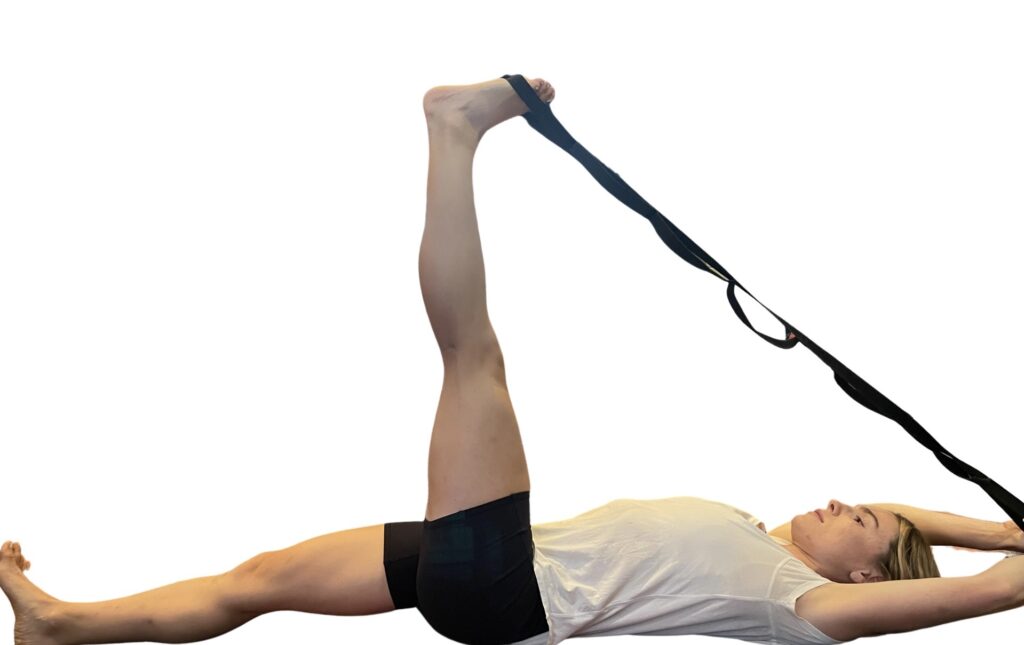

A demonstration of a hamstring stretch using a yoga strap.
Tightness in the back of your legs may be a sign of instability in your core, causing the leg muscles to overwork and shorten. As well, hamstrings are an important muscle to stretch if you have back pain, as they attach to the pelvis, which attaches to the back. An excellent stretch to ease the tension in the back of your legs is the hamstring stretch using a strap.
- Lie on your back and place a yoga strap or rope under one foot, with the other leg straight, on the floor, heel flexed.
- Slowly extend the leg toward straight.
- If it is too difficult to completely straighten the leg, bend the opposite leg.
Foam roller alignment
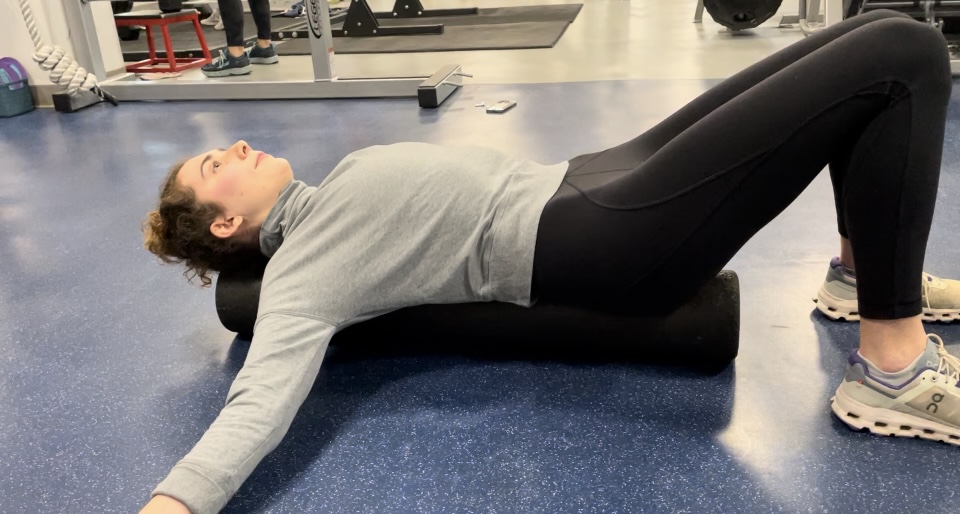

Lying lengthwise on a foam roller not only feels good but encourages good spinal length. We’re all guilty of bending forward while scrolling on our phones, resulting in a “forward head.†For every inch that your head is forward there’s 10 more pounds of pressure on the neck. Reset your alignment every day by lying on a foam roller. Lengthening the lumbar erector spinal muscles helps encourage neutral alignment and good posture.
- With your knees bent, lie on a roller, head supported and neck in a neutral position.
- Tighten the abdominals.
- Gently roll side to side for 20-30 seconds.
The sock test
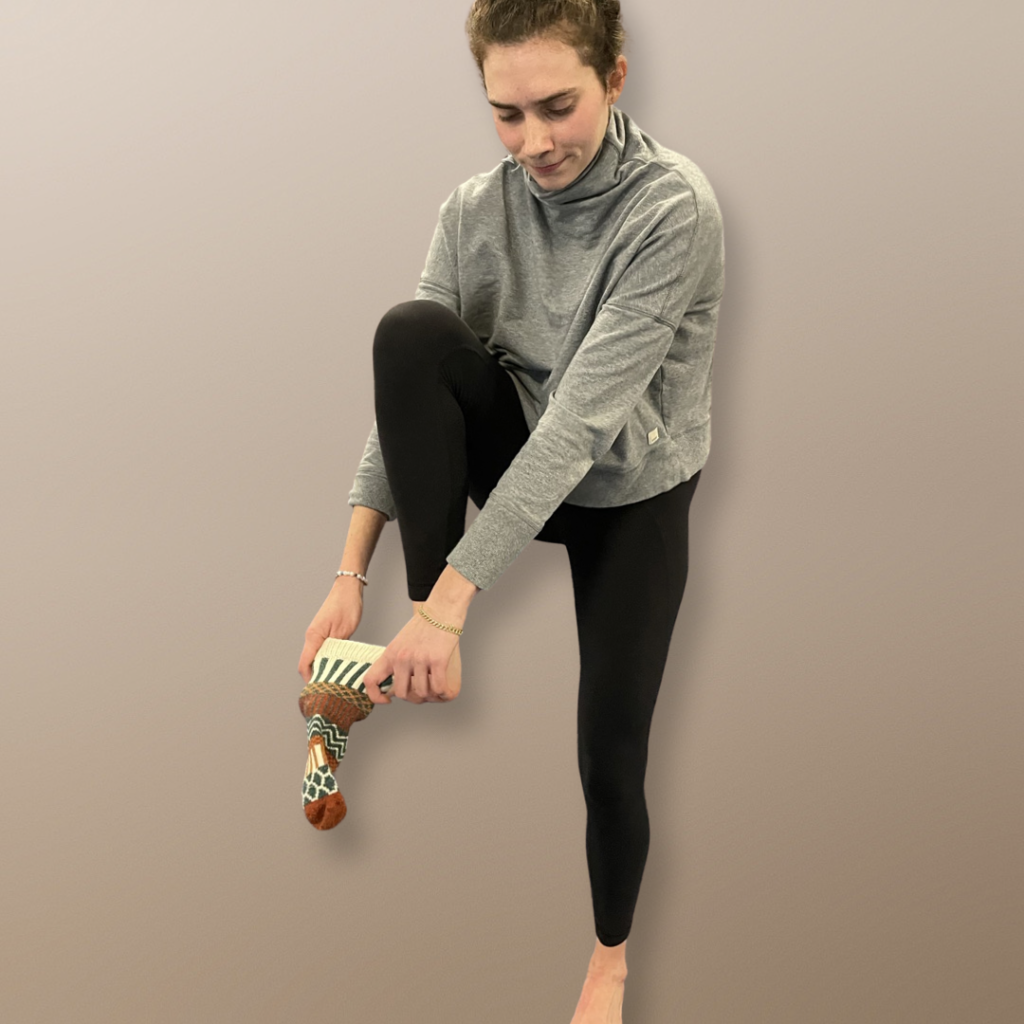


Losing your balance as you get older is no joke. Research has shown that the ability to stand on one foot drastically decreases after the age of 60, along with a rapid increase of falls and injury. The ability to stand on one leg is imperative for gait and function.
The sock test takes the exercise a step further. Practicing it is a fun challenge to build strength capacity and balance.
- Holding a sock, stand on one leg, knee slightly bent.
- Bring your right leg up toward you as you put your sock on
- Lower the leg to the floor and repeat with your left foot.