If your core is strong, you typically have good balance. Standing on one leg engages the core, and that ability is an indicator of overall well-being.
One-leg balancing involves using all 29 muscles of the core, called the lumbo-pelvic hip complex. But did you know that standing on one leg for 10 seconds can predict longevity? A recent study shows that the link between balance and longevity is an indicator of survival among middle-aged and older adults. Those that couldn’t do this simple task faced a higher mortality risk over seven years, emphasizing the critical role of balance for our health as we age.
Losing your balance as you get older is no joke. Research has shown that the ability to stand on one foot drastically decreases after the age of 60, along with a rapid increase of falls and injury. The ability to stand on one leg is imperative for gait and function.
Practicing the single-leg balance also improves your proprioception, or your body’s awareness of its position in space. Many daily movements involve being on one foot, even briefly, such as climbing stairs, putting pants on and stepping into a tub. Having better balance means daily activities that require coordination don’t have to result in falls or missteps.
You might think standing on one leg is a simple movement, but the ankles, lower leg, thighs, hips and core work together to make it happen. Try the following moves to test your skills!
Single-leg balance
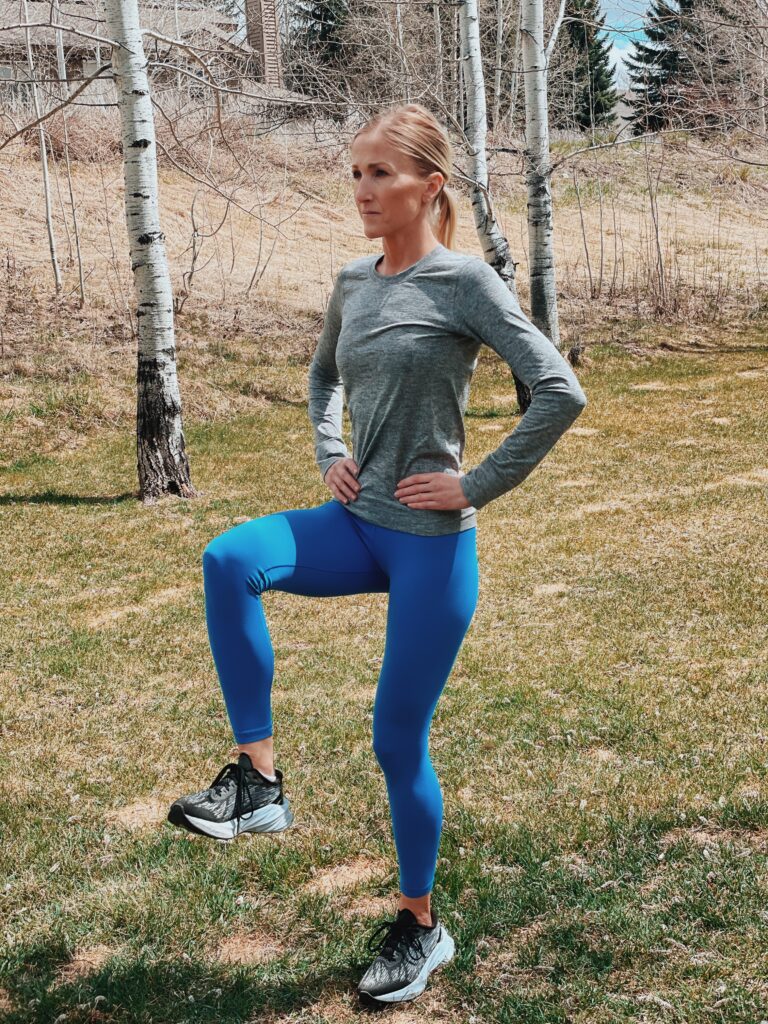

Photo by Connie Aronson
- Stand tall with your shoulders retracted. Feet are parallel and pointing forward. Hands are on the hips.
- Brace the core, and flex the hips and knees slightly.
- Lift one foot off the floor, keeping the toe of the raised foot pointed upward (dorsiflexed) and shift the center of your weight over the foot on the ground.
- Maintain the slightly squat position for 10 seconds.
- Return to the start; repeat on the opposite leg.
- Tip: Keep the chin pushed back, with the head tilted neither forward or backward.
There are countless exercises to train balance. The following variation targets the gluteals and is a total body movement.
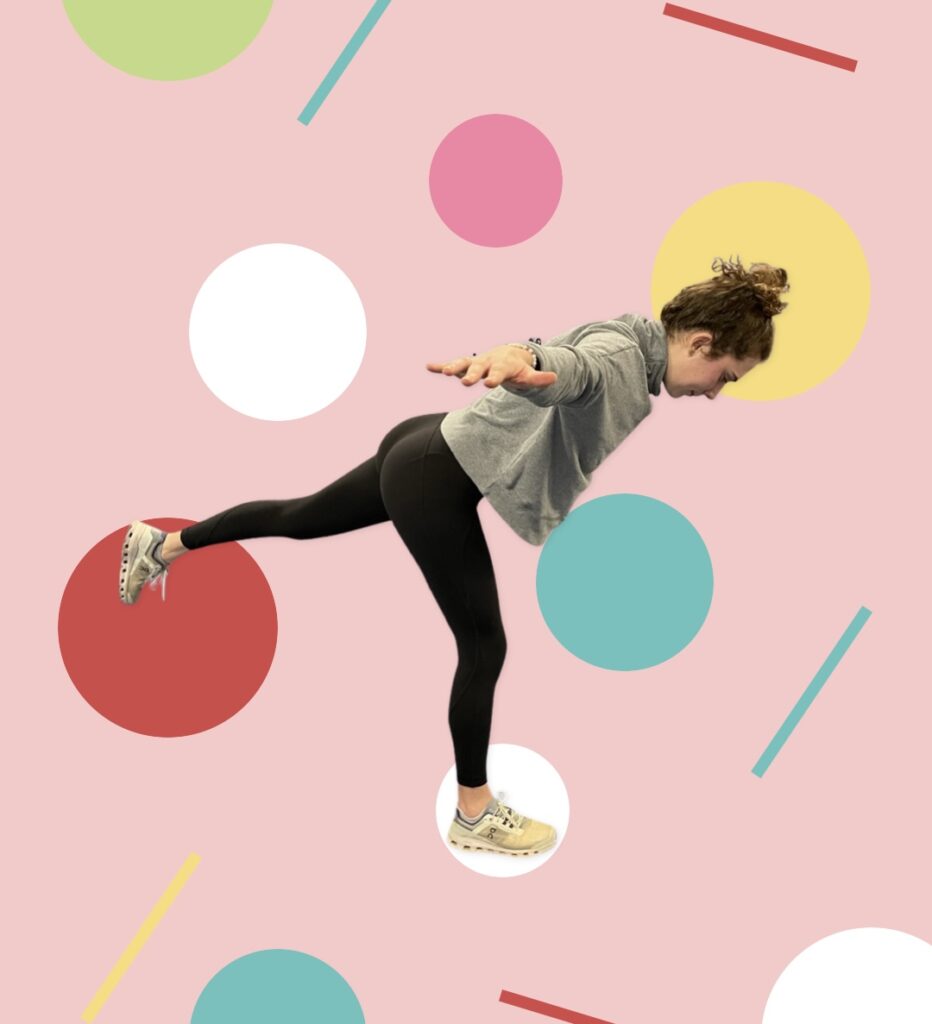
Single-leg balance and reach
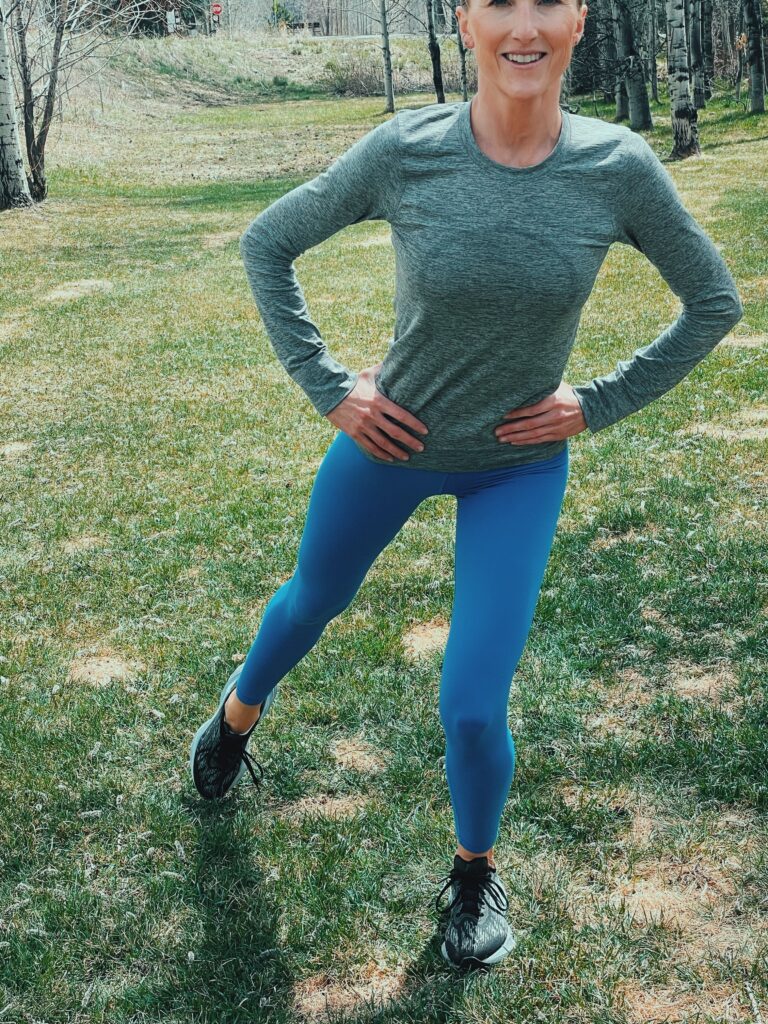

Efficient movement requires appropriate levels of stability (standing on one leg), while simultaneously having appropriate levels of mobility (extending your leg outward). During this move you have to engage the stabilizers for good postural control as you move your leg. Because it is multiplanar (dynamic planes of motion), it correlates to movements in sports and daily activities.
- Begin in a three-quarter squat, single-leg position as described for single-leg balance.
- Maintaining balance, reach forward with the up leg and tap the floor with that foot.
- Return back to neutral position.
- Maintaining balance, reach out laterally with the same foot as far as possible, without compromising form. Tap the floor.
- Return back to the start position.
- Lastly, open your hip and reach to the side and behind you. Tap the floor and return to the starting position.
- Continue with the same leg for four repetitions.
- Repeat on the opposite leg.
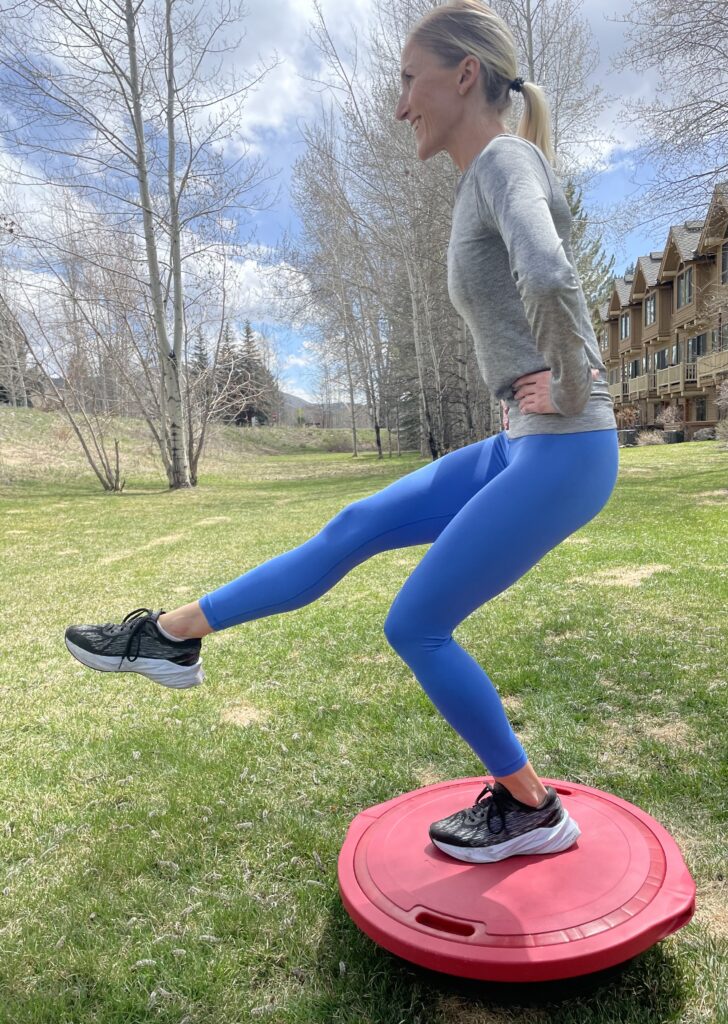

Single leg balance on an unstable surface ( BOSU )
*Tip-try to keep the flat side of the BOSU level. This means that your weight is distributed throughout your whole foot