- By CONNIE ARONSON #fitnessguru
Daily habits can be powerful. Routine builds structure, helps us stay on track and use our time wisely. Adding a simple mini exercise program to your day is one way to succeed. For many of us, we’re missing some key exercises that can keep us flexible, injury-free and improve function. Here are six top core and flexibility exercises that will enhance your athletic performance. Whether you are a seasoned athlete, or simply just enjoy being active and don’t want to get injured, incorporate these moves into your day.
Activate the core: Heel-on-toe crunch
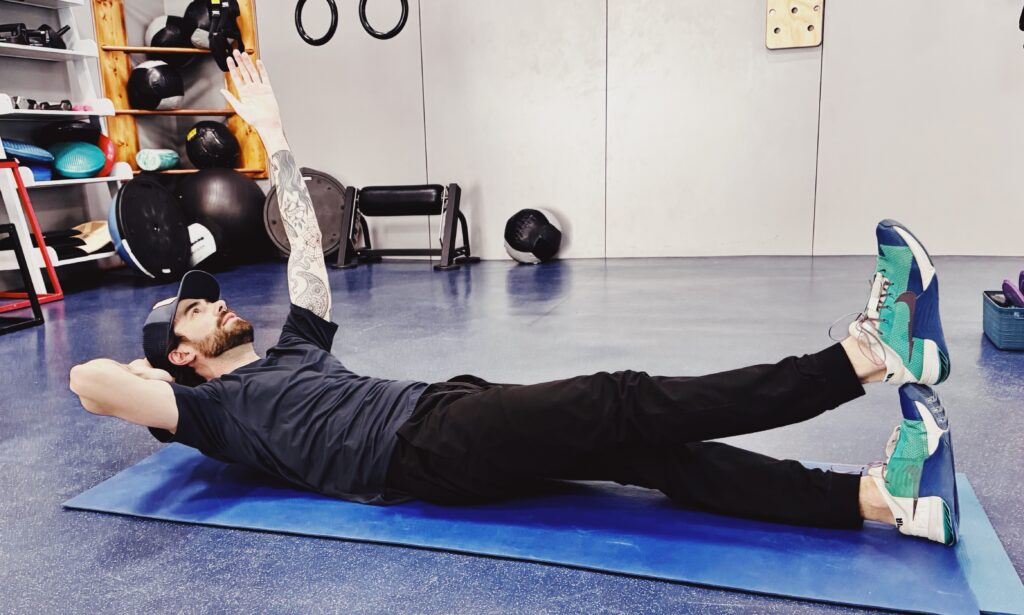

Photo courtesy of Connie Aronson
The core muscles help stabilize the spine and support movement. The following two core exercises build muscular fitness, have minimal movement, and are far more effective than a standard sit-up. To a viewer, it might not look like you’re doing much of anything, writes Stuart McGill in his book, “Back Mechanic,†but with proper technique, you should feel like you’re working.
- Begin with your legs straight, left heel on top of right foot.
- Bring your left hand behind your head for support, and lift your right arm straight up from your shoulder.
- Curl up, raising your head, neck and shoulder blades off the mat, tightening your abdominals.
- Hold for 10 seconds.
- Slowly return to the start position. Six reps.
Side-lying hip lift
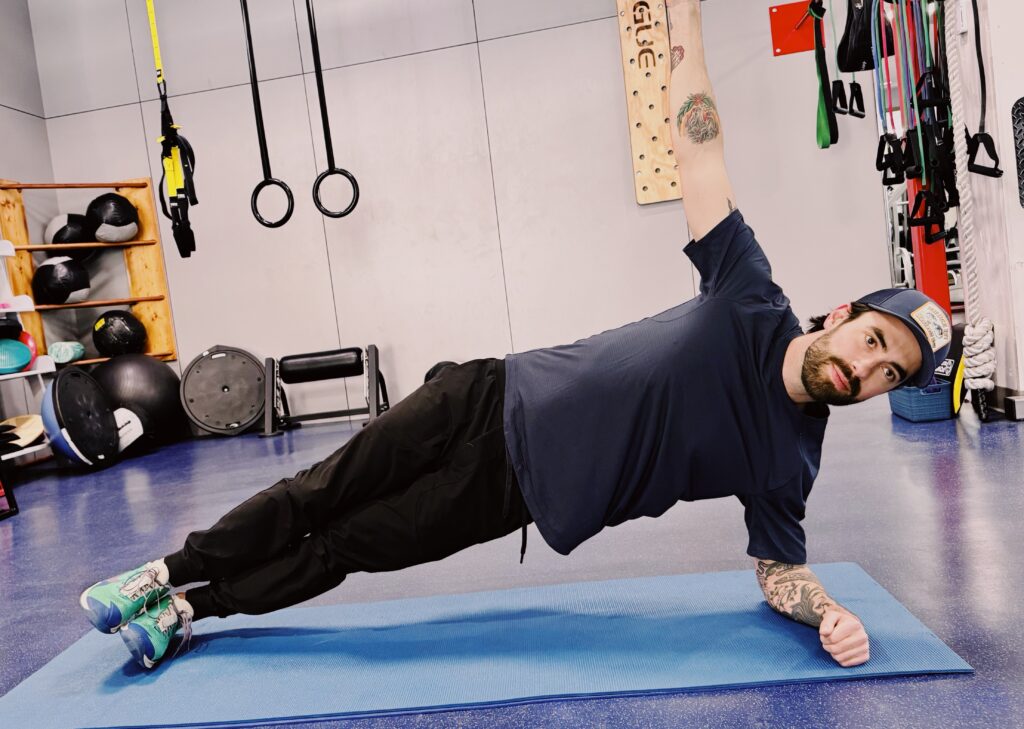


Photo courtesy of Connie Aronson
- To regress the move, lift from bent knees.
- Lying on your right side with your top leg stacked, place your right elbow under your right shoulder.
- Exhale and lift your right hip off the floor.
- Hold for 10 counts.
- Slowly lower to start. 6-8 reps. Switch sides.
Wall hamstring stretch
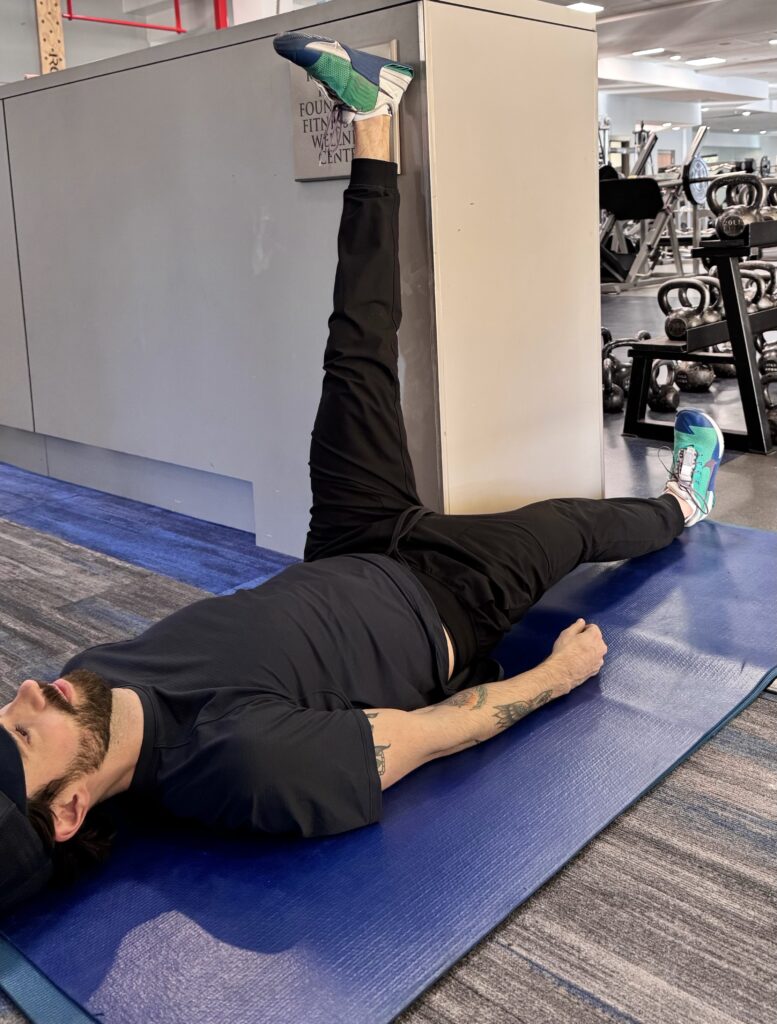
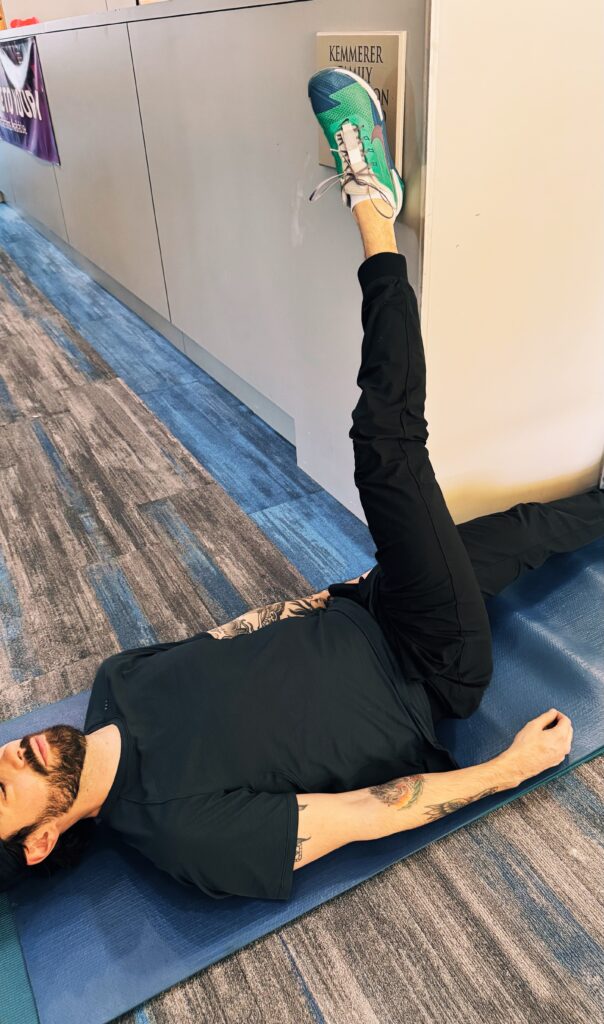



You can increase the stretch, and involve more gastrocnemius, by taking the outside leg across the body.
The wall hamstring stretch is an effective way to stretch your hamstrings. The stability of the wall and prone position help you relax deeper into the stretch, and you can easily adjust the intensity by moving your hips further or closer to the wall. Tight hamstrings may be a sign of imbalances, such as an anterior pelvic tilt or tracking problems of the knee. The hamstrings start at the sit bones and attach on either side of the lower leg. The muscles act as guide ropes on the legs as the foot rolls inward or outward (pronation and supination).
- Lie on the floor with the stretching leg on the corner of a wall or doorframe, with the other leg flat on the floor, heeled flexed.
- Use a pillow for your neck if needed.
- Move the hips closer or further from the wall to adjust the intensity.
- Keep the bottom leg straight. If you can’t, bend the bottom knee.
- Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat two to three cycles on each leg. Tip: Squeezing the quads will increase the stretch.
Foam roller alignment
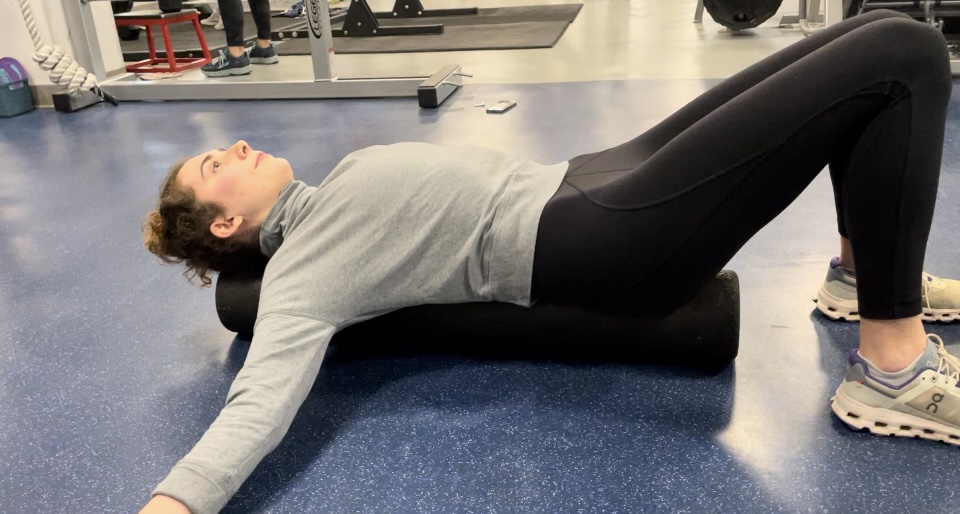

Reset your alignment every day by lying on a foam roller.
Lying lengthwise on a foam roller not only feels good but encourages good spinal length. If you’re hunched over with age, or are guilty of bending forward while scrolling on your phone, it can result in a “forward head.†For every inch that your head is forward, there’s 10 more pounds of pressure on the neck. Lengthening the lumbar erector spinal muscles helps encourage neutral alignment and good posture.
- With your knees bent, lie on a roller, head supported and neck in a neutral position.
- Tighten the abdominals.
- Gently roll side to side for 20-30 seconds, two to three times.
Foam roller thoracic spine
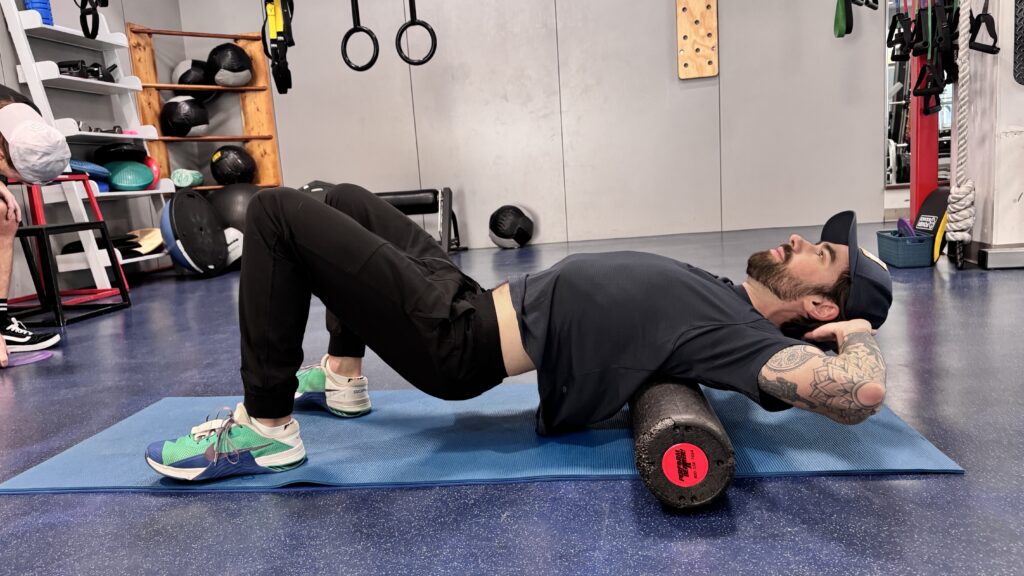


Using a foam roller on your thoracic spine helps upper back stiffness, as you can target the rhomboids and trapezius muscles. Rolling is a self-myofascial release technique that immediately relaxes sore spots and movement restrictions, allowing soft tissue and inflamed joints to rest and recover.
- Place a foam roller under your shoulder blades or at bra height.
- Support your head and tuck your chin.
- Bend your knees, tilt the pelvis slightly and lift your hips and pelvis off the floor.
- Gently roll on any tight or sore spots for 20-30 seconds.
Prayer stretch
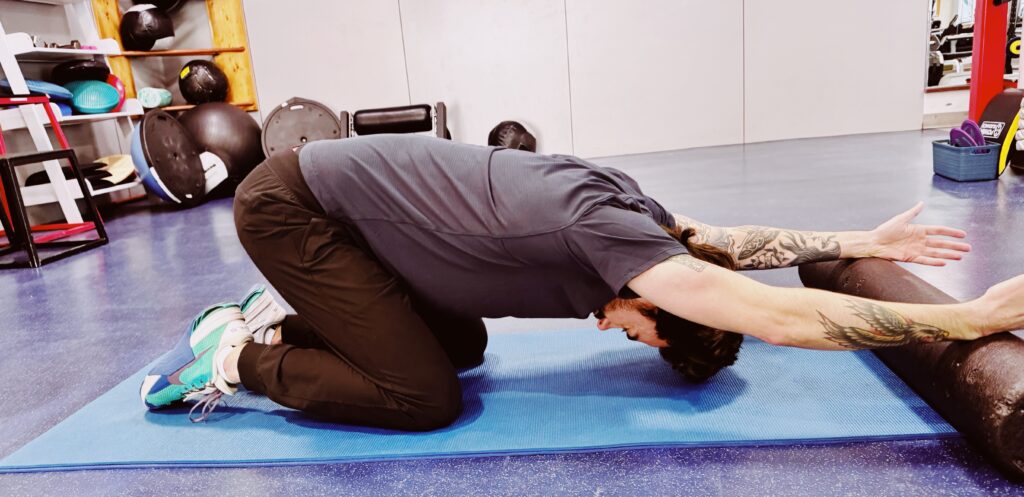


- Kneel on the floor with your hands on a roller.
- Slowly extend your arms forward, letting your chest move toward the floor.
- Relax in the stretch for 20-30 seconds and repeat two to three times.
- If you don’t have a roller, walk your hands forward, fully extending your arms, allowing your head to rest gently on the floor.