We take our balance for granted—until we have an embarrassing fall.
For youngsters, they typically shake off a fall. A young person has no problem slipping a sock on standing up. That’s a demonstration of balance and strength. Those past a certain age, however, usually sit down to pull on socks or sneakers. The fear of falling is a real concern. One of three older adults suffer a fall each year. Falls claimed 60,000 lives in 2012 and 2013. Falls are a serious health concern for older adults, alongside the cascade of other debilitating factors and a loss of independence.
Balance training is the mainstay of a fall prevention program, as well as strength and coordination. Lower body weakness increases the odds of falling fourfold. Unfortunately, there are other risk factors that contribute to falls. This includes foot problems, improper footwear like sneakers or slippers without traction and tight ankles. A limited range of motion in your ankles can affect balance and the simple ability to step up. Vision and environmental hazards in the house, like loose rugs or clutter, can contribute to falls as well.
One of the best things you can do as an adult is to make sure your gluteal medius and gluteal maximus muscles are strong. These posterior muscles are prime movers and important for stability. Making sure your glutes are working well, in conjunction with ankle mobility and stability, will help you move around with grace and confidence, and not fall.
Try to the following exercises every day.
Heel rise rocker
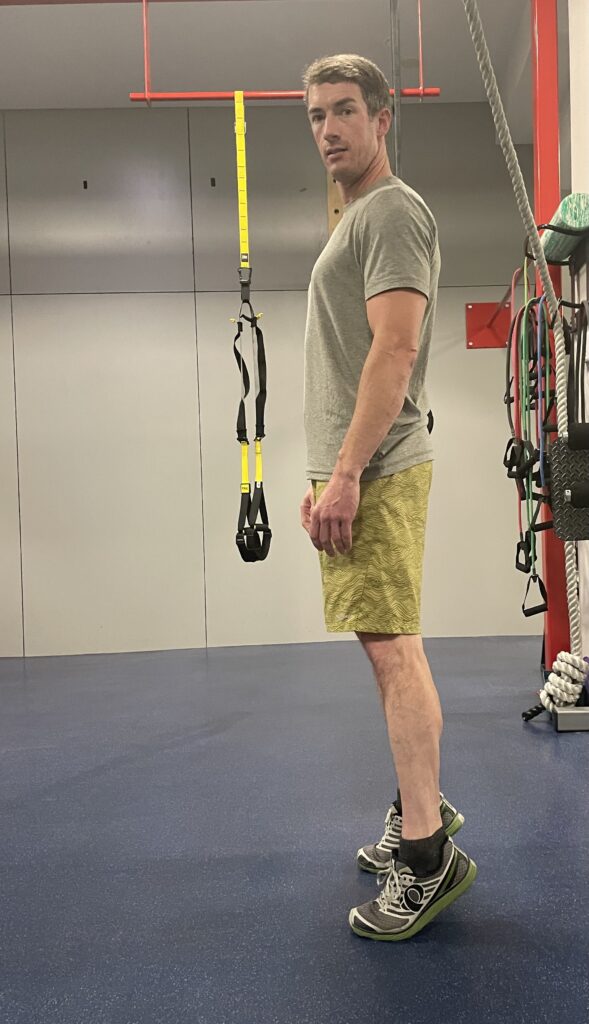

• Rise upward onto your toes and immediately rock back onto your heels as you lift your toes up towards your shins. Aim for 10-15 reps daily. Use a wall for support if needed.
Alphabet
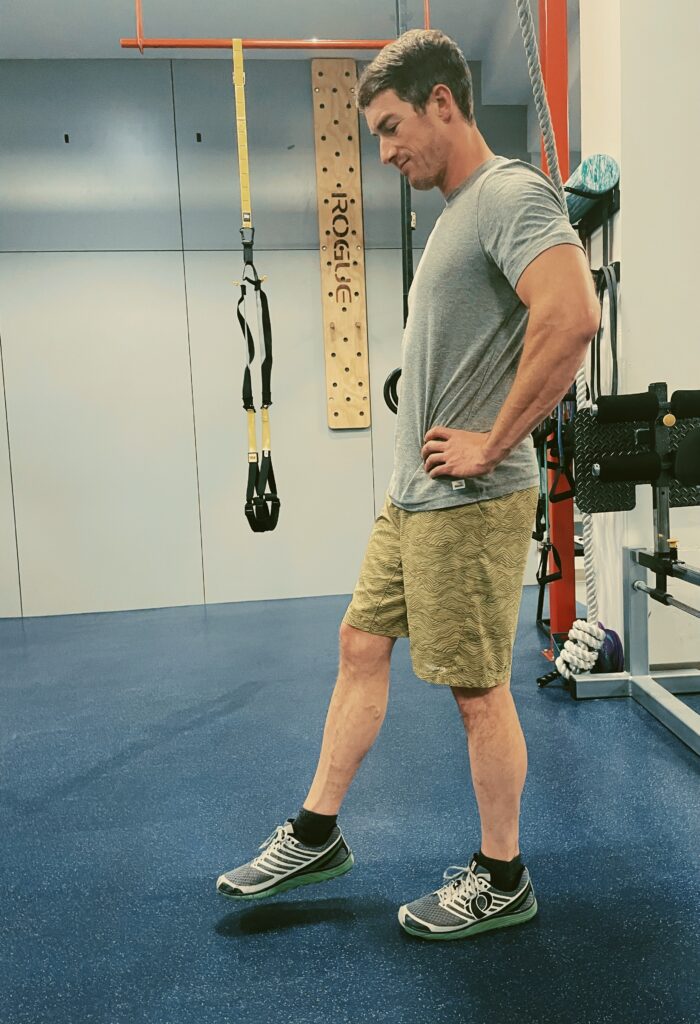

• Stand on your right leg with your opposite foot off the ground close to your right foot.
• Push your hips back slightly, into a quarter squat. Keep your torso engaged, and the weight balanced on the whole foot.
• With your foot in the air, write the letters of the alphabet with your foot using small movements.
• Repeat on the left leg.
Bridging—single leg
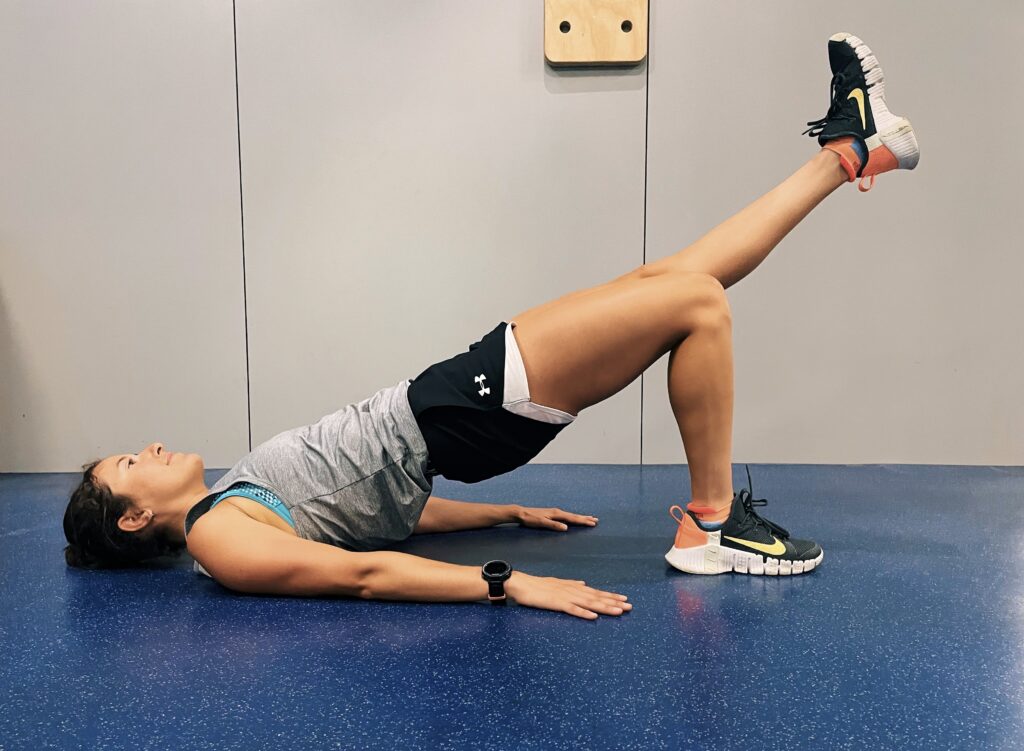

• Lie face-up with your arms by your side, knees bent and feet flat on the ground.
• Squeeze your glutes and lift your hips off the ground until your knees, hips and shoulders are in a straight line.
• Extend one leg, foot flexed, and keep it extended.
• Lower and lift your hips 12 times. Repeat on the other side.
Clam Shell
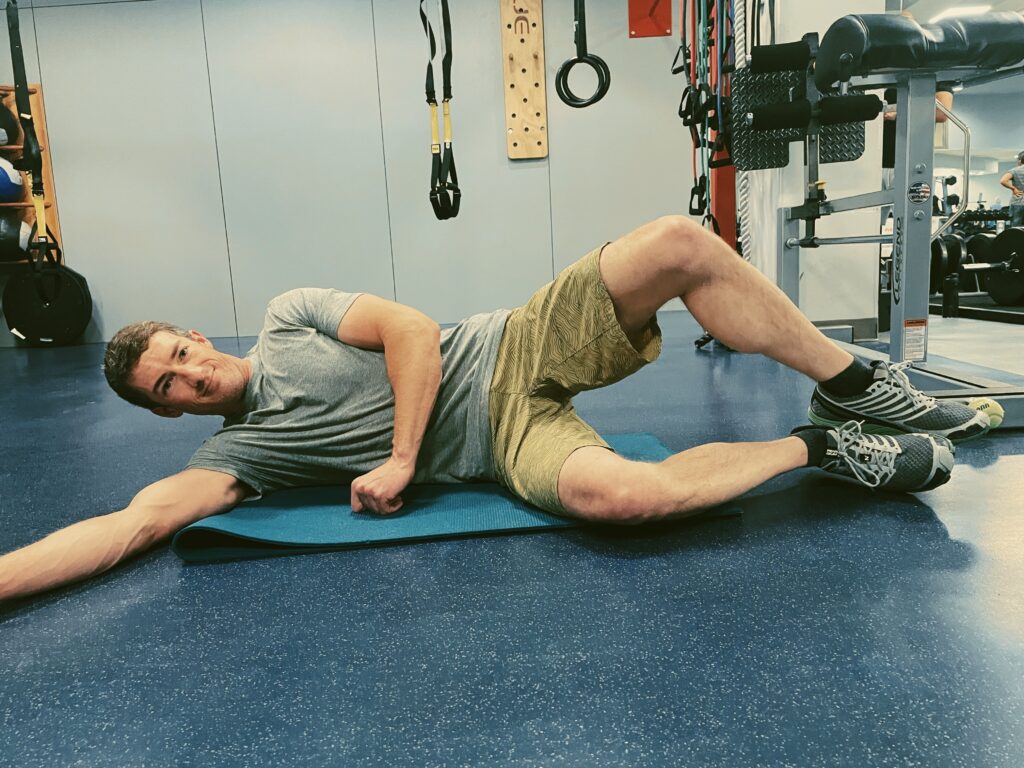
• In a side-lying position, hips slightly flexed and the knees bent, raise your top knee off the bottom knee by contracting the hip muscles. This exercise mimics the opening of a clamshell.
• Avoid rolling or rotating your torso as you lift your knee.
Tree Pose
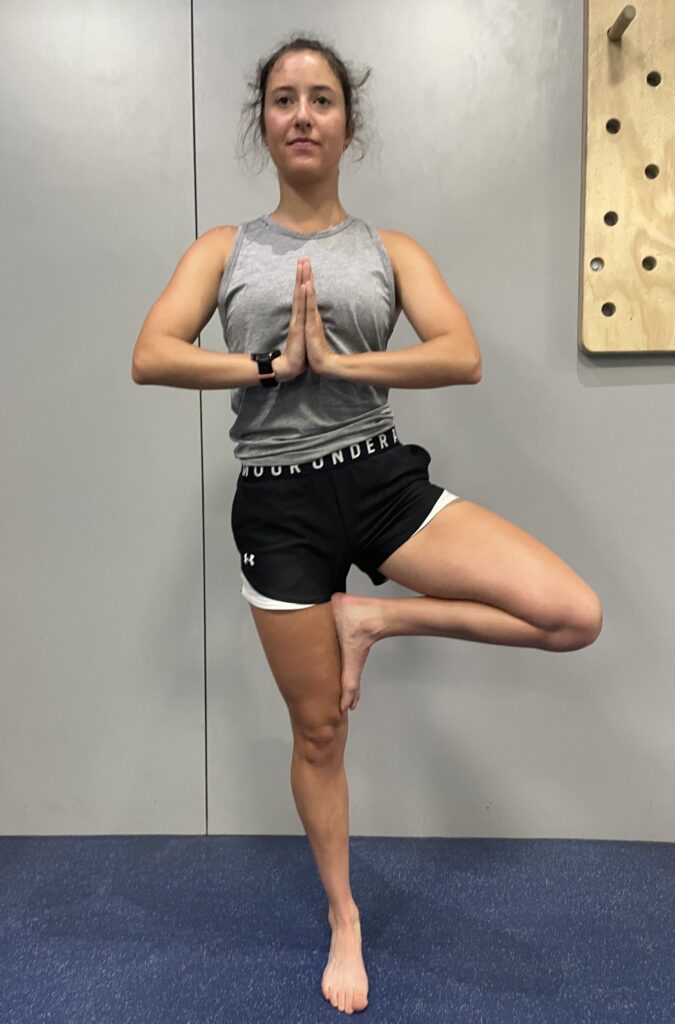

Tree pose develops balance, stability and poise. It strengthens the muscles of the supporting leg and foot.
• Stand firm on the right leg. Use a wall for support if needed.
• Bend the left leg out to the side, hold the foot and press the sole of your right foot into the top of your right inner thigh.
• Straighten the right knee and press the left knee back, in line with the left hip.
• Try to balance for 20 seconds before repeating on the left leg.
Published in the Idaho Mountain Express June 16, 2023


